How to divide O, E, S, C, L, U Bands in optical communication
Time: 2023-12-19
The wavelength of light is different, the transmission loss in the optical fiber is also different. Scientists after continuous exploration and testing, found that 1260nm ~ 1625nm This region of light, the signal distortion is the smallest, the lowest loss, the most suitable for transmission in optical fiber.
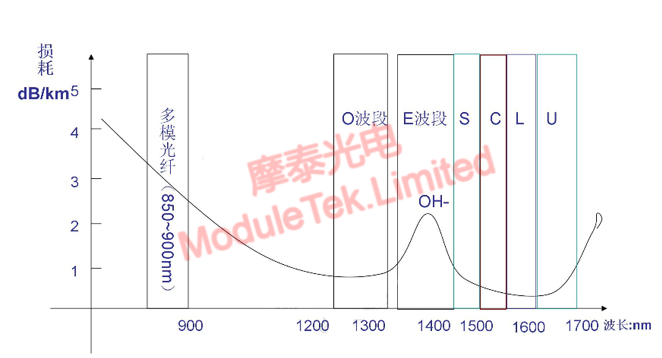
Figure 1 Attenuation of different wavelengths in fiber optic transmission
In May 2002, ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standards Division) divided these low attenuation wavelength region (1260nm ~ 1625nm) into five bands: O, E, S, C, L. The wavelengths are divided into five bands: O, E, S, C, L, and L.
Table 1 Comparison of each band
|
Band
|
Description
|
Wavelength range
|
|
O band
|
original
|
1260-1360 nm
|
|
E band
|
extended
|
1360-1460 nm
|
|
S band
|
Short wavelength
|
1460-1530 nm
|
|
C band
|
conventional
|
1530-1565 nm
|
|
L band
|
Long wavelength
|
1565-1625 nm
|
|
U band
|
Ultralong wavelength
|
1625-1675 nm
|
O band: O band is the original wavelength band with a wavelength range of 1260nm-1360nm. O band is the first wavelength band historically used for optical communications and has the least signal distortion (due to dispersion).
E band: belongs to the extended wavelength band, with a wavelength range of 1360nm-1460nm, and is the least common of these bands. The E band is mainly used as an extension of the O band, but is rarely used, mainly because many existing fiber optic cables show high attenuation in the E band and the manufacturing process is very energy intensive, thus limiting its use in optical communications.
S band: belongs to the shortwave band, the wavelength range is 1460nm-1530nm, its fiber loss is lower than that of O band, S band is used as many PON (Passive Optical Network) systems.
C band: The wavelength range is from 1530nm to 1565nm, which represents the conventional band. Optical fiber exhibits the lowest loss in the C band, which is advantageous in long-haul transmission systems and is commonly used in many metro, long-haul, ultra-long-haul, and submarine optical transmission systems in conjunction with WDM and EDFA technologies. The use of the C-band has expanded with the advent of DWDM (dense wavelength division multiplexing), which allows multiple signals to share a single fiber.
L band: The long wavelength band, ranging from 1565nm to 1625nm, is the second-lowest-loss wavelength band and is often used when C-band is insufficient to meet bandwidth requirements. With the widespread use of EDFA, DWDM systems have expanded upward into the L-band, which was initially used to expand the capacity of terrestrial DWDM optical networks. It has now been introduced to submarine cable operators to extend the total capacity of submarine cables. Because the two transmission windows, the C band and the L band, have the lowest transmission attenuation loss, signaling light in DWDM systems is usually selected in the C band and the L band.
U band: In addition to the above five bands, there is a U band, U refers to "ultra-long-wavelength", the wavelength range is 1625nm-1675nm, it is mainly used for network monitoring applications.
Moduletek Limited is at your service!
If you have any questions about the above content, you can contact us by Email : web@moduletek.com

 40G/100G Optical Transceivers
40G/100G Optical Transceivers 10G/25G Optical Transceivers
10G/25G Optical Transceivers 155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers
155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers 100M/1G Optical Transceivers
100M/1G Optical Transceivers FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers
FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers
CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers 100M/1G/10G Coppers
100M/1G/10G Coppers Active Cable AOC
Active Cable AOC Direct Attach Cable DAC
Direct Attach Cable DAC Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords
Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords MT2011
MT2011 MT2010
MT2010 CodingBox
CodingBox






