Optical module common failure of optical power abnormality
Time: 2024-08-26
The article Digital Diagnostic Function (DDM) For Optical Modules describes that DDM function can be used for real-time monitoring and fault location of the module's working status, in which the optical module's transmitting optical power and receiving optical power are the key parameters for judging the performance of the optical module. This paper introduces the common failure causes of abnormal transmit/receive optical power of optical modules and proposes countermeasures to help users quickly locate or solve network failures.
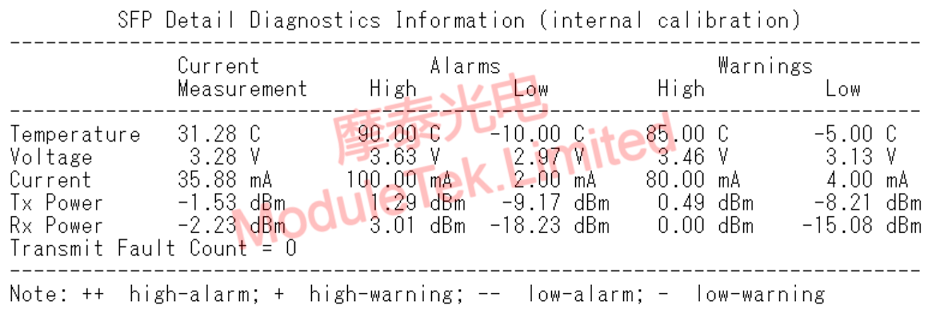
Figure 1 Switch reading module DDM
1. Transmit optical power
When the optical modules at both ends of the link work normally, the transmit optical power is within a certain range, which can be learned by checking the corresponding product datasheet or reading the module threshold on the switch. When the transmit optical power exceeds the nominal working range, it may cause the optical module to work abnormally, thus affecting the network data transmission, and users can carry out preliminary troubleshooting and localization in the following ways.
· Low transmit optical power
Impact: It may lead to low optical power received at the opposite end, which may cause packet loss or the port cannot be LINK UP.
Reason: bad transmission signal of optical module or failure of optical module itself (if it is measured optical power instead of DOM data, it should also be considered whether the end surface of the transmitter is dirty or whether the optical fiber is damaged or failed).
Countermeasure: Replace the optical module.
· High Transmitted Optical Power
Impact: It may lead to high received optical power at the opposite end, thus causing the optical module at the opposite end to burn out due to continuously high received power.
Reason: Optical module failure at this end.
Countermeasure: Replace the optical module;
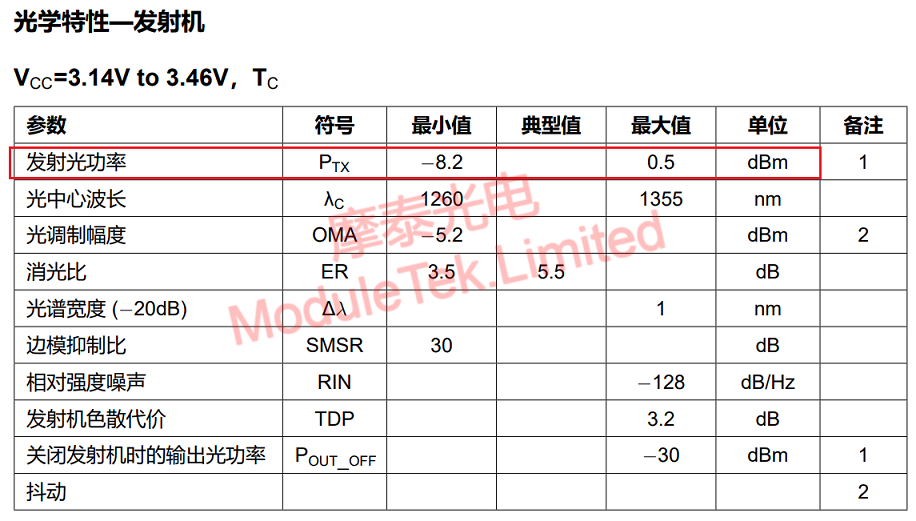
Figure 2 10G LR Transmit Optical of Moduletek Limited Power Parameter Display
2. Receiving optical power
When the optical modules at both ends of the link work normally, the received optical power is within a certain range, which can be learned by checking the corresponding product data manual or reading the module threshold on the switch. When the received optical power exceeds the nominal working range, it may cause the optical module to work abnormally, thus affecting the network data transmission, and the user can carry out preliminary investigation and localization in the following ways.
· Low received optical power
Impact: The signal received at the local end is too low, and packet loss may occur or the port may not be able to LINK UP.
Reason: The actual transmission distance exceeds the nominal transmission distance of the optical module, the optical fiber is not inserted tightly, the receiving end of the optical module is dirty or damaged, and the end surface of the optical fiber is dirty or damaged.
Countermeasures: Use the module according to the nominal transmission distance, clean the end face of the module, clean the end face of the optical fiber, or replace the optical fiber, or replace the optical module.
· High received optical power
Impact: The optical module may be burned out due to continuously high received power.
Reason: Possible causes are long distance optical module for short distance transmission, the opposite end of the module luminous abnormalities, this end of the module receiving end failure.
Countermeasures: Add light attenuation on the optical module to protect the optical module, replace the optical module.
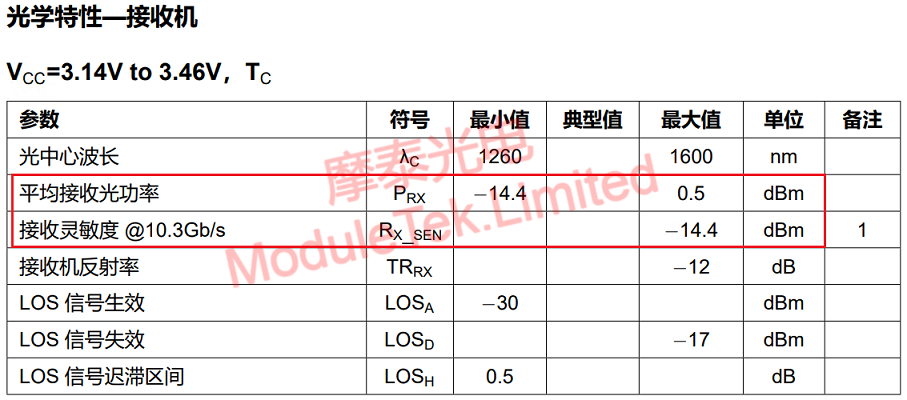
Figure 3 10G LR receiving optical of Moduletek Limited power parameters show
Moduletek Limited is at your service.
If you have any questions about the above content, you can contact us by Email : web@moduletek.com
If you have any questions about the above content, you can contact us by Email : web@moduletek.com

 40G/100G Optical Transceivers
40G/100G Optical Transceivers 10G/25G Optical Transceivers
10G/25G Optical Transceivers 155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers
155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers 100M/1G Optical Transceivers
100M/1G Optical Transceivers FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers
FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers
CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers 100M/1G/10G Coppers
100M/1G/10G Coppers Active Cable AOC
Active Cable AOC Direct Attach Cable DAC
Direct Attach Cable DAC Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords
Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords MT2011
MT2011 MT2010
MT2010 CodingBox
CodingBox






