Introduction to data transmission methods in PON networks
Time: 2023-06-25
PON network accesses multiple users at the same time through a single optical fiber to achieve point-to-multipoint (P2MP) transmission applications. The direction of data transmission, from the OLT to the ONU is called downlink, from the ONU to the OLT is called uplink, and the downlink and uplink are realized in the way of full duplex transmission. The following figure shows the schematic data transmission principle of a PON network, which has the following typical characteristics:
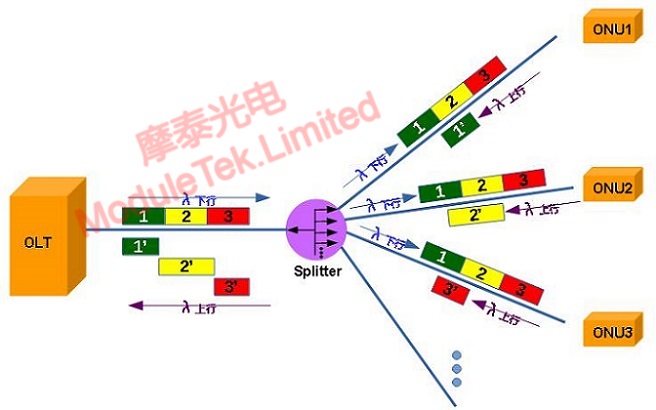
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the data transmission principle of PON network
1. PON network uses different wavelengths to achieve upstream and downstream data transmission in the same fiber. The downstream wavelength is generally selected as 1490nm or 1577nm, the upstream wavelength is generally selected as 1310nm or 1270nm, and the third wavelength, 1550nm, is used for CATV services of the broadcasters.The reason for this selection is that the standard will be formulated to put the lower-cost devices on the multipoint side of the transmitter to reduce the deployment cost of the PON network.
2. PON downlink uses broadcast to transmit data. The downlink is limited by the physical characteristics of the passive splitter, the data sent by the OLT through the passive splitter is evenly distributed to each ONU, each ONU can receive data from other ONUs. In order to ensure the security of the data, ONU will actively filter the data that does not belong to it, at the same time, the data sent by OLT will be encrypted, and the secret key will be generated by each ONU and sent to the OLT, which ensures that it is difficult to decrypt the data of the ONU by other ONUs.
3. PON uplink using TDMA way to transmit data, TDMA channel segmentation mechanism can avoid the superposition of optical signals of the same wavelength and the occurrence of data "collision", so as to equitably share the backbone fiber and resources. It divides the uplink into different time slots, and then divides these time slots into different ONUs according to the needs, and the ONUs send data in their own time slots.
It should be noted that the ONU's luminous time is strictly specified by the OLT, which does not actively emit light, nor does it emit light for a long time.Therefore, the transmitter of the OLT optical module on the PON link works in continuous mode, while the transmitter of the ONU optical module works in burst mode. Once an ONU actively emits light or a long time, it is a "rogue ONU", which will affect the business of the entire PON port.
Moduletek Limited is at your service!
If you have any questions about the above content, you can contact us by Email : web@moduletek.com

 40G/100G Optical Transceivers
40G/100G Optical Transceivers 10G/25G Optical Transceivers
10G/25G Optical Transceivers 155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers
155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers 100M/1G Optical Transceivers
100M/1G Optical Transceivers FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers
FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers
CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers 100M/1G/10G Coppers
100M/1G/10G Coppers Active Cable AOC
Active Cable AOC Direct Attach Cable DAC
Direct Attach Cable DAC Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords
Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords MT2011
MT2011 MT2010
MT2010 CodingBox
CodingBox






