Technical characteristics of 1310 wavelength and 1550 wavelength in 10Gb optical module applications
Time: 2020-02-23
I. Optical communication wavelengths
There are three windows of wavelength in 10Gb optical module communication applications, namely, 850nm window, 1310nm and 1550nm window. 850nm is applied to multi-mode optical fiber, 1310nm and 1550nm are applied to single-mode optical fiber. Usually single-mode fiber practical application users will have questions, 1310nm wavelength and 1550nm wavelength, what are the advantages and disadvantages, how do we choose the wavelength? In this article, we will explore this issue.
II. 1310nm vs 1550nm
2.1 Attenuation characteristics
Different wavelengths of optical signals in the unit length of fiber optic transmission will have different attenuation coefficients, we take the G652 fiber as an example, the following figure 1 for different wavelengths of optical signal transmission attenuation:
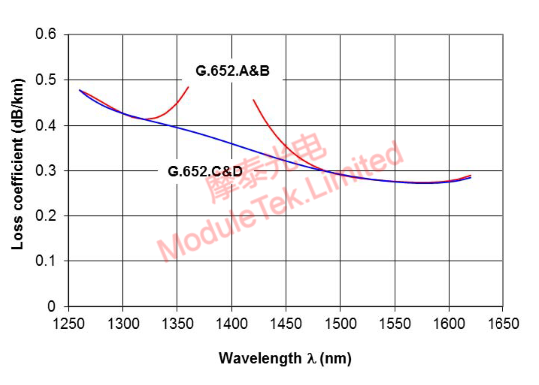
Figure 1 shows the transmission attenuation coefficient of different wavelengths
As shown in the figure above: in the G652 C&D fiber 1270nm wavelength attenuation coefficient α = 0.46dB/km, 1310nm wavelength attenuation coefficient α = 0.42dB/km, 1550nm wavelength attenuation coefficient α = 0.28dB/km. Optical signal transmission attenuation in the optical fiber: Loss = α * L (where the unit of Loss in dB, α units of dB / km, L units km). L is in dB, α is in dB/km, and L is in km).
Table 1 Different wavelengths and different transmission distances attenuation calculation
|
Distance |
500m(dB) |
2km(dB) |
10km(dB) |
40km(dB) |
80km(dB) |
|
1310nm |
0.21 |
0.84 |
4.2 |
16.8 |
33.6 |
|
1550nm |
0.14 |
0.56 |
2.8 |
11.2 |
22.4 |
2.2 Dispersion Characteristics
Dispersion, also known as pulse broadening, is a physical characteristic of optical signal transmission in optical fiber, specific performance: the input signal pulses are separate, do not overlap each other; the output pulse shows pulse broadening, resulting in overlapping pulses, pulses can not be distinguished from each other; optical fiber bandwidth with the increase in dispersion decreases. This is shown in the figure below:
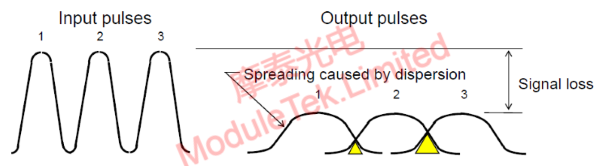
Figure 2 Dispersion-transmission pulse broadening diagram
Different wavelengths of optical signals transmitted in the fiber dispersion is different, as shown in Figure 3 below:
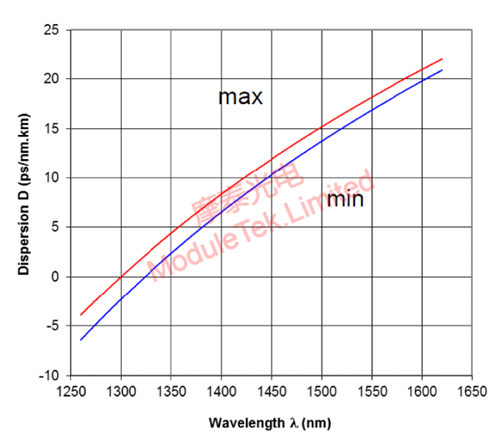
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the dispersion coefficient of different wavelength transmission
Where the dispersion coefficient D (unit ps/nm.km), in the G652 C&D fiber 1310nm wavelength dispersion coefficient (maximum) D = 0.91ps/nm.km, 1330nm wavelength dispersion coefficient (maximum) D = 2.7ps/nm.km, 1550nm wavelength dispersion coefficient (maximum) D = 18.2ps/nm.km. Optical signals transmitted over the fiber Transmission of dispersive pulse broadening: CD = D * L (where CD unit ps, D unit ps/nm.km, L unit km).
III. 10 Gigabit 1310 wavelength and 1550 wavelength optical module parameter comparison
10 Gigabit 1310 wavelength optical module technology used without a cooler DFB laser, the cost is lower, the optical module into the fiber power can be 1-2mW or so, the laser operating current is usually in the 30-50mA or so, the module at room temperature power consumption in 0.8W or so, due to the fiber attenuation of the larger, the transmission distance is usually less than 40km, the 1310 wavelength optical module can be used in large quantities in a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers of application scenarios; 10 Gigabit 1310 wavelength optical module parameters comparison. The 10 Gigabit 1550 wavelength optical module technology usually requires the use of EML laser with a cooler, the optical module into the fiber power can be 1-2mW or so, the laser operating current is usually in the 70-100mA or so, the module power consumption at room temperature is less than 1.2W, high temperature 75 ℃ under the TEC current increases the module power consumption will be up to 1.5W, usually applied to 40-80km fiber optic transmission environment, the module can be used in a large number of applications. 80km fiber optic transmission environment, due to 40-80KM application scenarios less, more parts and more complex processing, the module is relatively expensive. The specific parameters of the two wavelength 10Gb optical modules are shown in the following figure:
Table 2 Comparison of 1310 wavelength optical module and 1550 wavelength optical module
|
Wavelength |
Luminous power |
Extinction ratio |
Bias current |
Power consumption |
Transmission Distance |
|
1310nm(DFB) |
0~5dBm |
<4dB |
30~50mA |
<1.2W |
<40km |
|
1550nm(EML) |
-4~4dBm |
8~12dBm |
60~100mA |
<1.5W |
40~80km |
Therefore, we have to choose the type and wavelength of the module according to the transmission distance of the link, the attenuation coefficient of the fiber, the dispersion coefficient, the power consumption control requirements and the cost budget in the actual project application.
Moduletek Limited can provide the above two wavelengths of optical module products, welcome to buy.
If you have any questions about the above content, you can contact us by Email : web@moduletek.com

 40G/100G Optical Transceivers
40G/100G Optical Transceivers 10G/25G Optical Transceivers
10G/25G Optical Transceivers 155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers
155M/622M/2.5G Optical Transceivers 100M/1G Optical Transceivers
100M/1G Optical Transceivers FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers
FC 16G/32G Optical Transceivers CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers
CWDM/DWDM Optical Transceivers 100M/1G/10G Coppers
100M/1G/10G Coppers Active Cable AOC
Active Cable AOC Direct Attach Cable DAC
Direct Attach Cable DAC Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords
Regular/MTP-MPO Fiber Patch Cords MT2011
MT2011 MT2010
MT2010 CodingBox
CodingBox






